Fusion Energy: A Giant Leap Closer to Reality
The dream of harnessing the power of the stars for clean and limitless energy has taken a giant leap forward. In December 2022, scientists at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) achieved a breakthrough in fusion research, successfully producing a net energy gain from a fusion reaction for the first time ever ([Department of Energy, National Nuclear Security Administration. "DOE National Laboratory Makes History by Achieving Fusion Ignition"]. This means the reaction generated more energy than it took to initiate and sustain it, marking a significant milestone on the path towards commercially viable fusion power plants.
What is Fusion Energy?
Fusion energy replicates the process that powers stars, including our Sun. It involves fusing atomic nuclei, typically isotopes of hydrogen (deuterium and tritium), to create a heavier element (helium) and releasing a tremendous amount of energy in the process. Compared to traditional energy sources, fusion offers several advantages:
Abundant Fuel: The fuel for fusion, hydrogen isotopes, is readily available in seawater.
Clean Energy: Fusion produces minimal radioactive waste compared to nuclear fission.
Low Risk of Meltdown: Fusion reactions are inherently safer than nuclear fission reactions.
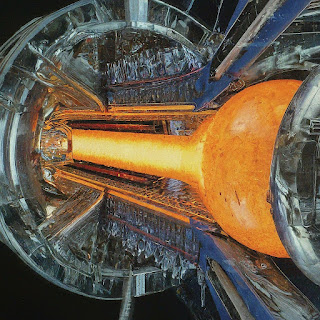
The LLNL Breakthrough
The LLNL experiment employed a technique called inertial confinement fusion. They fired high-powered lasers at a tiny pellet of hydrogen fuel, creating extreme heat and pressure that forced the nuclei to fuse ([Department of Energy, National Nuclear Security Administration. "DOE National Laboratory Makes History by Achieving Fusion Ignition"]). While this is a major step forward, significant hurdles remain before fusion becomes a practical energy source.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Scaling up the LLNL experiment to a commercially viable power plant presents a significant engineering challenge. Additionally, sustaining the fusion reaction for extended periods and developing efficient methods to capture the generated heat and convert it into electricity are crucial hurdles that need to be overcome.
Advancements in materials science, laser technology, and plasma control are key areas of focus for researchers. International collaboration and increased investment will also be necessary to accelerate progress towards a fusion-powered future.
Looking Forward
While achieving net energy gain is a significant milestone, the timeline for widespread commercialization of fusion energy remains uncertain. Estimates suggest it may take decades before fusion becomes a mainstream energy source. However, this breakthrough has renewed optimism, and with continued research and development, the dream of clean and limitless energy from fusion may one day become a reality.
Brought to you by The Simplicity Lifestyle
Further Reading:
Department of Energy, National Nuclear Security Administration. "DOE National Laboratory Makes History by Achieving Fusion Ignition." https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-04045-8 (accessed May 26, 2024).
"Nuclear-fusion breakthrough: this physicist helped to achieve the first-ever energy gain." Nature Journal, https://www.nature.com/immersive/d41586-021-03401-w/index.html (accessed May 26, 2024).
Financial Times. "Fusion Energy." https://www.ft.com/content/a9815bca-1b9d-4ba0-8d01-96ede77ba06a (accessed May 26, 2024).



Comments
Post a Comment